How to make global bilateral tariffs time series using WITS API in R
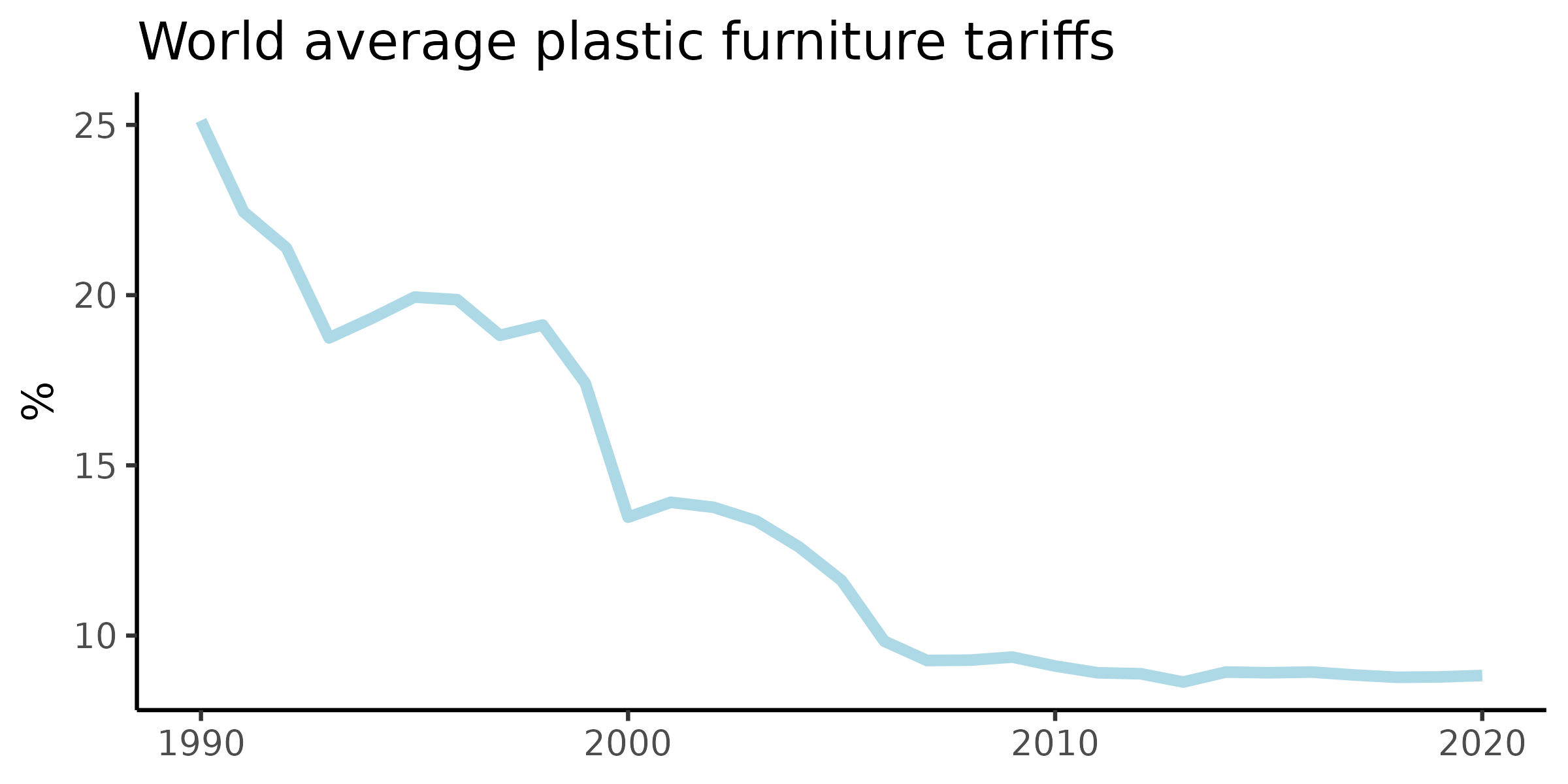 Evidence bases require quality tools. In the spirit of disseminating generic tools to help improve everyone’s quality of research, here’s a generic tool that I made to create a time series of bilateral tariffs for any HS6 code that you need. It’s harder than it seems. This is because:
Evidence bases require quality tools. In the spirit of disseminating generic tools to help improve everyone’s quality of research, here’s a generic tool that I made to create a time series of bilateral tariffs for any HS6 code that you need. It’s harder than it seems. This is because:
- The UNCTAD tariffs dataset in WITS is not comprehensive, and has lots of missing data. So you have to fill in the gaps, e.g. missing years.
- HS codes change over time (so you’ll need to design your own concordance. An example of this is common wheat (100190) which existed until 2011, after which it mostly became 100199 (common wheat, not seed)).
- Multiple tariffs exist for any given route/product combination. (You need to work out what tariff applies amongst numerous available preferential rates on any given bilateral route. This will cover WTO most favoured nation (MFN) tariffs, preferential trade agreements (bilateral and regional) and the Generalised System of Preferences (GSP)).
- You need to map out the different members of each regional trade agreement and dates of accession, etc.
Here’s a general rundown of what you need to do:
- Work out what HS codes and years you want
- Download all the data (you can also do a great big unzip of bulk data)
- Prepare for imputing missing data - backup partner (exporter) names
- Prepare for imputing missing data - replace RTA partner codes with generic names
- Impute missing data
- Identify and remove overzealous imputations
- Split the dataset to MFNs and preferential tariffs
- Populate RTAs and GSPs with their members/beneficiaries
- Find lowest preferential tariff for year/HS code/bilateral pair
- Apply MFNs to all beneficiaries
- Rejoin the MFNs and preferential tariffs
- Calculate minimum tariff for each partner/reporter/HS6 code/year
The full script can be accessed here.
Details of all of the above are as follows, but first some preliminaries, and make sure you uncomment the install line, if you need to install packages.
#Code to get historical tariff dataset on a bilateral product level.
#Install and load packages
#install.packages(c("rsdmx","httr","xml2","utils","tidyr","dplyr")) #uncomment if you need to install them
library(rsdmx)
library(httr)
library(xml2)
library(utils)
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
#Insert file names
#Download the following csv file from https://github.com/jamesfell0000/build_tariff_time_series/blob/main/pref_imput_groups.csv
RTA_groupings_CSV <- 'pref_imput_groups.csv' #This is a custom file created by me, interpreting inconsistent RTA descriptions and grouping them as consistent RTAs. The basis for this is the file at http://wits.worldbank.org/data/public/TRAINSPreferenceBenficiaries.xls
#Download the following csv file from https://github.com/jamesfell0000/build_tariff_time_series/blob/main/RTA_members.csv
RTA_members_CSV <- 'RTA_members.csv' #Create this file yourself from http://wits.worldbank.org/data/public/TRAINSPreferenceBenficiaries.xls
Work out what HS codes and years you want (see HS nomenclature at WCO website):
#1. What codes do you want?
product_list <- list("940370") #Can do as a list e.g. list("100199","100190")
#What years do you want?
years_list <- as.list(1988:2020)
#Insert codes that are considered to be the same product, e.g. wheat used to be 100190, and is now effectively 100199.
common_commodity_code <- function() {
#No concordance needed for plastic furniture (HS codes haven't changed, but wheat example is given below)
#tariffs_df$PRODUCTCODE[tariffs_df$PRODUCTCODE == "100190"] <- "100199"
}
Download all the data (you can also do a great big unzip of bulk data). Warning: this takes about 3 hours on a slow computer for one HS code and all reporters and 1988-2020.
#2. Download all the data
#This requires looping through each reporter and each year.
#First need Reporter list:
#Download all the country codes from WITS
countries <- read_xml("http://wits.worldbank.org/API/V1/wits/datasource/tradestats-tariff/country/ALL")
country_details <- xml_find_all(countries, ".//wits:country")
#Get country code list
country_code_list <- as.data.frame(xml_attr(country_details, "countrycode"))
#Get details about whether a country is classified as a reporter
country_code_list_isreporter <- as.data.frame(xml_attr(country_details, "isreporter"))
#Combine the previous two lists
reporter_df <- cbind(country_code_list,country_code_list_isreporter)
#Change the column names to something logical
colnames(reporter_df)[1:2] <- c("countrycode", "isreporter")
#Filter to just reporters
reporter_df <- reporter_df[reporter_df$isreporter=="1",]
#Get the list of reporters from the dataframe
reporter_list <- as.list(reporter_df$countrycode)
#Create a dataframe to store our data:
tariffs <- data.frame()
Sys.time()
#The wits API can't cope with large downloads, so we need to advance one year at a time, one reporter at a time, one product at a time by looping through the years and countries.
products <- paste(product_list, collapse = "+")
for (reporter in reporter_list) {
for (year in years_list) {
#First build the url
url <- paste0("http://wits.worldbank.org/API/V1/SDMX/V21/rest/data/DF_WITS_Tariff_TRAINS/A.",reporter,"..",products,".aveestimated/?startperiod=",year,"&endperiod=",year,"&detail=Full")
#Check there are data available before downloading:
data_availability_check <- GET(url)
if (status_code(data_availability_check) == 200) {
#Download the data
dataset <- readSDMX(url)
#Convert the data to a dataframe
year_df <- as.data.frame(dataset)
year_df$EXCLUDEDFROM <- NULL #Get rid of this column, not hugely useful and doesn't always appear
#Bind this year's data to the previous year's data.
tariffs <- rbind(tariffs,year_df)
}
}
}
Sys.time()
Prepare for imputing missing data - backup partner (exporter) names
#3. Duplicate the column with the partners, call it 'partner_original'. This is so we can populate the RTAs later, but in the meantime we need to replace the partners with an RTA grouping code for imputation purposes.
tariffs$PARTNER_original <- tariffs$PARTNER
Prepare for imputing missing data - replace RTA partner codes with generic names
#4. Replace the RTA partner codes with the RTA_grouping_code (this is necessary for imputation because different RTA partner codes are used for the same RTA).
#Read in the RTA groupings from the csv
RTA_groupings <- read.csv(RTA_groupings_CSV) #File available in this repository
RTA_groupings <- subset(RTA_groupings, select=c("PARTNER", "RTA_group","Impute_until"))
#Merge in the imputation group to the tariffs df
tariffs <- merge(tariffs,RTA_groupings,by="PARTNER",all.x=TRUE)
tariffs$PARTNER[!(is.na(tariffs$RTA_group))] <- tariffs$RTA_group[!(is.na(tariffs$RTA_group))]
Impute missing data
#5. Impute missing data
#build a dataframe with each reporter product partner year
#merge in tariffs by reporter product partner year
#fill gaps with tidyr, choose down
#remove row if tariff is na
partner_list <- as.list(unique(tariffs$PARTNER)) #this gets the list of partners who actually appear in the dataset (serves the purpose of imputation)
#Get list of partners. We do this now to save on
all_combinations_df <- expand.grid(REPORTER = reporter_list, PARTNER = partner_list,obsTime = years_list, PRODUCTCODE = product_list)
all_combinations_df <- as.data.frame(lapply(all_combinations_df, unlist))
#Merge all_combinations_df with tariffs
all_combinations_df <- merge(all_combinations_df, tariffs, by=c("REPORTER","PRODUCTCODE","PARTNER","obsTime"), sort=TRUE, all=TRUE)
#Add imputed tag if no tariff data, in preparation for imputing values
all_combinations_df$is_imputed <- "no"
all_combinations_df$is_imputed[is.na(all_combinations_df$obsValue)] <- "imputed"
#Impute missing values
tariffs_df <- all_combinations_df %>%
dplyr::group_by(REPORTER,PRODUCTCODE,PARTNER) %>%
fill(obsValue,NOMENCODE,PARTNER_original, .direction = "down") %>%
dplyr::ungroup()
#remove cases of no data (this is because not all partners were available for all reporters, or if there was no data for a reporter/partner combo for years early on)
tariffs_df <- tariffs_df[!(is.na(tariffs_df$obsValue)),]
Identify and remove overzealous imputations
#6. Remove incorrect imputations
#Overwrite the product codes so they are all of the same hs version, e.g. 100190 becomes 100199.
#(change this to a function which will be defined above)
common_commodity_code()
#Do a count on the number of observations for each year, productcode, reporter, partner. Merge in the count. If the count is >1 and imputed = yes, then delete the observation.
tariffs_df$HS_version_obs <- as.numeric(substr(tariffs_df$NOMENCODE,2,2))
latest_HS_versions <- aggregate(list(HS_version=tariffs_df$HS_version_obs), list(obsTime=tariffs_df$obsTime,PRODUCTCODE=tariffs_df$PRODUCTCODE,REPORTER=tariffs_df$REPORTER,PARTNER=tariffs_df$PARTNER),max)
#merge in the latest HS versions
tariffs_df <- merge(tariffs_df,latest_HS_versions,by=c('obsTime','PRODUCTCODE','REPORTER','PARTNER'),all.x=TRUE)
#Get rid of it if it is imputed and not using the latest HS version.
tariffs_df <- tariffs_df[!(tariffs_df$is_imputed == "imputed" & (tariffs_df$HS_version_obs < tariffs_df$HS_version)),]
Split the dataset to MFNs and preferential tariffs
#7. Extract out the MFNs and put them in a different dataset. Create a dataset with no MFNs, call it the preferential dataset.
MFNs <- tariffs_df[tariffs_df$PARTNER=="000",]
saveRDS(MFNs,'MFNs.rds')
pref_tariffs <- tariffs_df[!(tariffs_df$PARTNER=="000"),]
saveRDS(pref_tariffs,'pref_tariffs.rds')
Populate RTAs and GSPs with their members/beneficiaries
#8. expand out the RTA codes in the preferential dataset using the excel file of members of each RTA, using the partner_original column (I think you can just do a merge.y=ALL)
RTA_members <- read.csv(RTA_members_CSV)
RTA_members <- subset(RTA_members, select=c("PARTNER", "Country"))
RTA_members$PARTNER_original <- RTA_members$PARTNER
RTA_members$PARTNER <- NULL
pref_tariffs <- merge(pref_tariffs, RTA_members, by=('PARTNER_original'), all.x=TRUE)
#Change column names: PARTNER to PARTNER_AND_RTA, country to PARTNER
colnames(pref_tariffs)[which(names(pref_tariffs) == "PARTNER")] <- "PARTNER_AND_REGION"
colnames(pref_tariffs)[which(names(pref_tariffs) == "Country")] <- "PARTNER"
#If PARTNER is na then adopt the PARTNER_ORIGINAL code. (It can be NA because it could be a straight PTA, not RTA)
pref_tariffs$PARTNER[is.na(pref_tariffs$PARTNER)] <- pref_tariffs$PARTNER_original #You might get a warning.
saveRDS(pref_tariffs,'pref_tariffs.rds')
Find lowest preferential tariff for year/HS code/bilateral pair
#9. Now we have a list of bilateral product level tariffs. We then need to summarise that list so that it gives us the lowest preferential tariff (use aggregate and min)
minimum_pref_tariffs <- aggregate(list(min_tariff=pref_tariffs$obsValue), list(obsTime=pref_tariffs$obsTime,PRODUCTCODE=pref_tariffs$PRODUCTCODE,REPORTER=pref_tariffs$REPORTER,PARTNER=pref_tariffs$PARTNER),min)
Apply MFNs to all beneficiaries
#10. Now we switch focus to the MFNs. This could be altogether in the steps above, but it is interesting to be able to show the difference between MFN and lowest preferential rate.
#Expand out the MFNs to all countries (could get a list of all the countries in the dataset, or do some otherway). (I think you can just do a merge.y=ALL)
#Get details about whether a country is classified as a partner
country_code_list_ispartner <- as.data.frame(xml_attr(country_details, "ispartner"))
country_code_list_isgroup <- as.data.frame(xml_attr(country_details, "isgroup"))
#Combine the previous three lists
partner_df <- cbind(country_code_list,country_code_list_ispartner,country_code_list_isgroup)
#Change the column names to something logical
colnames(partner_df)[1:3] <- c("countrycode", "ispartner","isgroup")
#Filter to just partners and no RTAs
partner_df <- partner_df[partner_df$ispartner=="1" & partner_df$isgroup=="No",]
partner_df$isgroup <- NULL
partner_df$ispartner <- NULL
partner_df$PARTNER <- "000"
#Do the merge:
MFNs <- merge(MFNs, partner_df, by=('PARTNER'), all.x=TRUE)
MFNs$PARTNER <- NULL
MFNs$PARTNER <- MFNs$countrycode
MFNs$countrycode <- NULL
MFNs <- subset(MFNs, select=c("obsTime", "PRODUCTCODE","REPORTER","PARTNER","obsValue"))
saveRDS(MFNs,'MFNs.rds')
colnames(MFNs)[which(names(MFNs) == "obsValue")] <- "min_tariff"
Rejoin the MFNs and preferential tariffs
#11. Bind together the MFNs to the preferential dataset (merge on year, reporter, partner)
MFNs_and_pref_tariffs <- rbind(MFNs,minimum_pref_tariffs)
Calculate minimum tariff for each partner/reporter/HS6 code/year. The code produces a dataframe of minimum applied tariffs for every year, the products you specified and every reporter/partner combo.
#12. Calculate the minimum tariff for each partner/reporter/year.
min_bilateral_tariffs <- aggregate(list(min_tariff=MFNs_and_pref_tariffs$min_tariff), list(year=MFNs_and_pref_tariffs$obsTime,PRODUCTCODE=MFNs_and_pref_tariffs$PRODUCTCODE,REPORTER=MFNs_and_pref_tariffs$REPORTER,PARTNER=MFNs_and_pref_tariffs$PARTNER),min)